Understanding Dengue: Causes, Prevention, and Management
Dengue is a mosquito-borne viral infection that has become a significant public health concern, particularly in tropical and subtropical regions around the world. With the increasing prevalence of dengue outbreaks, it’s crucial to understand the disease, how to prevent it, and how to manage its symptoms if contracted. This article delves into the causes, prevention, and effective management of dengue fever.
What is Dengue?
Dengue is caused by the dengue virus (DENV), which is transmitted primarily by the Aedes aegypti mosquito, although Aedes albopictus can also spread the virus. The virus exists in four distinct strains (DENV-1, DENV-2, DENV-3, and DENV-4). A person infected with one strain develops immunity to that strain but can still contract the other three, sometimes leading to more severe forms of the disease.
How Dengue Spreads
The dengue virus is transmitted when an infected mosquito bites a person. Mosquitoes become carriers by biting an already infected individual and can continue to spread the virus to others. Aedes mosquitoes typically bite during the day, especially at dawn and dusk.
Symptoms of Dengue
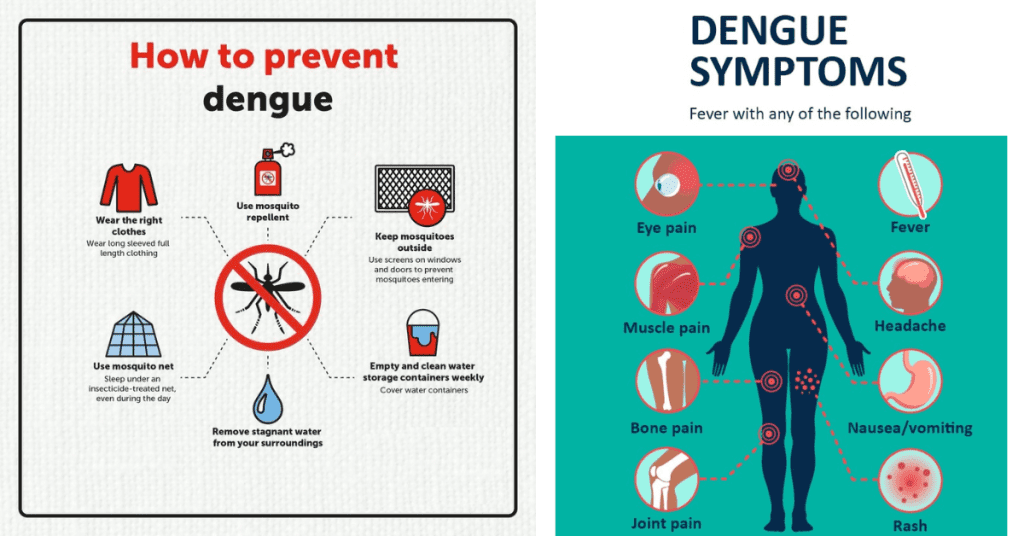
Dengue manifests after an incubation period of 4 to 10 days post-infection. Its symptoms can range from mild to severe and include:
- High fever (up to 104°F or 40°C)
- Severe headache and pain behind the eyes
- Joint and muscle pain (often called “breakbone fever” due to its intensity)
- Nausea and vomiting
- Rashes appearing 2-5 days after the fever starts
- Mild bleeding from gums or nose
In some cases, dengue can develop into more severe forms like Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever (DHF) or Dengue Shock Syndrome (DSS), which are life-threatening and require immediate medical attention.
Prevention of Dengue
Prevention is key when it comes to dengue, as there is no specific treatment to cure the virus. Here are effective preventive measures:

1. Eliminate Mosquito Breeding Grounds
The mosquitoes that carry dengue breed in stagnant water. To reduce the risk:
- Remove standing water: Regularly empty containers that hold water, such as buckets, flowerpots, tires, and birdbaths.
- Cover water storage containers to prevent mosquitoes from laying eggs.
2. Protect Yourself from Mosquito Bites
Taking steps to avoid mosquito bites is crucial in preventing dengue:
- Use insect repellent: Apply mosquito repellents containing DEET, picaridin, or oil of lemon eucalyptus, especially during peak biting times (dawn and dusk).
- Wear protective clothing: Wear long-sleeved shirts, long pants, and socks when outdoors, and opt for light-colored clothing, as mosquitoes are attracted to dark colors.
- Sleep under mosquito nets: In areas with a high prevalence of mosquitoes, sleep under a mosquito net, especially if you’re outdoors or in areas without screens.
3. Maintain Clean Surroundings
- Keep your home and surroundings clean and free of items that can collect water.
- Participate in community-wide efforts to control mosquito populations, as coordinated action is more effective.
Identifying and Managing Dengue
If you or someone you know begins showing symptoms of dengue, early identification and proper management can prevent complications and support recovery.
1. Early Diagnosis
- Consult a doctor if symptoms of dengue appear, especially if you live in or have traveled to an area with known dengue outbreaks.
- Doctors can confirm dengue with blood tests to detect the virus or antibodies.
2. Managing Dengue Symptoms
There is no specific antiviral treatment for dengue, but supportive care helps in recovery. Here’s how to manage dengue:
- Hydration: Dehydration is a major concern with dengue, as it can lead to severe complications. Drink plenty of fluids like water, oral rehydration salts (ORS), and fruit juices to stay hydrated.
- Fever and Pain Management: Use acetaminophen (paracetamol) to control fever and relieve pain. Avoid aspirin and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen, as these can increase the risk of bleeding.
- Rest: Get plenty of rest to help your body fight the infection and recover faster.
3. Recognizing Severe Dengue
Severe dengue, also known as Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever (DHF) or Dengue Shock Syndrome (DSS), is a more dangerous form of the disease. Be aware of these warning signs, which typically appear between the 3rd and 7th day of illness:
- Persistent vomiting
- Severe abdominal pain
- Bleeding from gums or nose
- Difficulty breathing
- Extreme fatigue or confusion
If any of these symptoms occur, seek emergency medical care immediately.
Conclusion
Dengue is a preventable disease, and by taking proactive steps such as eliminating mosquito breeding grounds, using repellents, and wearing protective clothing, the risk of contracting dengue can be significantly reduced. Early identification and management of the symptoms can also help prevent severe complications. Community efforts to reduce mosquito populations and educate the public are crucial in the fight against dengue. Stay informed and take action to protect yourself and your loved ones from this potentially dangerous virus.
